
Varicella, commonly known as chickenpox, is a highly contagious infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. While anyone can get chickenpox, it is most common in children.
Although chickenpox often leads to mild symptoms, it can be severe for infants, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems. It poses additional risks to newborns if their mothers have chickenpox around the time of delivery.
Chickenpox spreads easily through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, and sometimes through direct contact with the rash.
Symptoms usually appear 7 to 21 days after exposure, and individuals with chickenpox are contagious from 1 to 2 days before the rash appears until the spots stop forming and dry up. Once you have had chickenpox, it’s very unlikely you’ll get it again because your body has built up immunity.
The first sign of chickenpox is a blister-like rash filled with clear fluid that eventually breaks and dries. The rash usually appears on the face, scalp, and body, and can be quite itchy. Different stages of the rash (red spots, vesicles, scabs) may appear at the same time.
In vaccinated individuals who contract chickenpox, lesions may not crust, and they remain contagious until no new lesions have developed for 24 hours.
Other common symptoms include:
Treatment focuses on relieving fever, discomfort, and itching. Common treatments include fever reducers and anti-itch medications. Antiviral medications can be effective if taken within the first 72 hours of symptoms, especially within the first 24 hours. This helps to lessen the severity and duration of the illness, particularly in those with severe symptoms or weakened immunity.
Avoid aspirin as it can lead to a serious illness called Reye’s syndrome, which can cause severe liver and brain damage.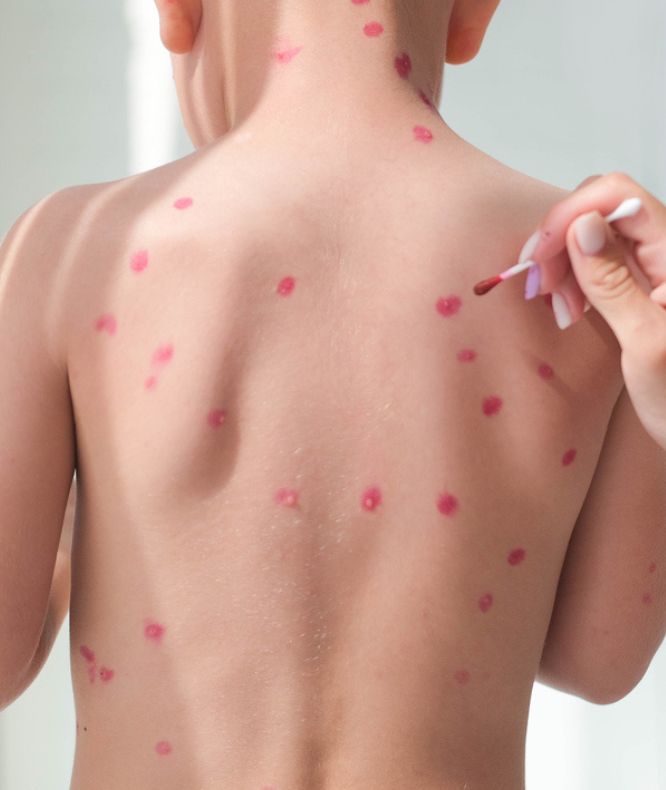
Schedule an appointment with a paediatrician to confirm the diagnosis and discuss the best course of treatment.
It is also important to prevent kids from scratching and picking at the blisters, which may allow bacteria to infect the sores and lead to bacterial infections.
Help your child relieve itchiness and discomfort:
The chickenpox vaccination is the most effective way to prevent chickenpox.
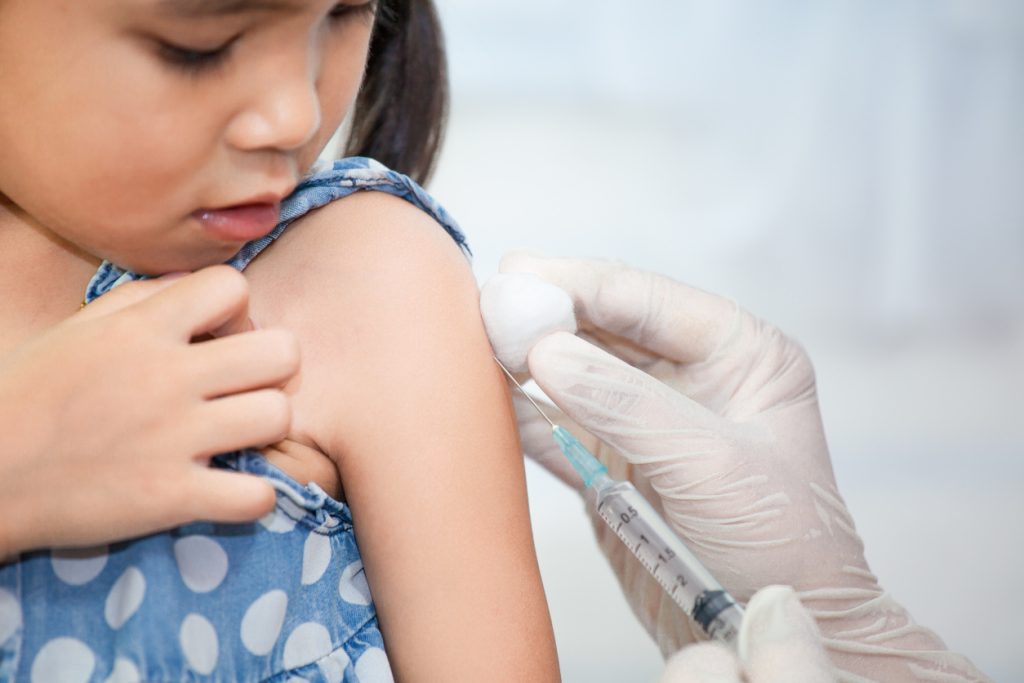
This schedule protects over 90% of children. Most vaccinated individuals do not contract chickenpox again, and if they do, symptoms are generally milder with fewer lesions and lower fever. If an unvaccinated child is exposed to chickenpox, they can still receive the vaccine within 24 to 72 hours to help reduce the likelihood of developing the disease.
Without vaccination, chickenpox has a 90% attack rate, meaning there’s a high chance of contracting the disease after exposure.
Although most healthy children recover within 1 to 2 weeks, in less common cases, severe complications can arise, especially in individuals with weakened immunity:
Chickenpox can lead to severe complications and even death, even in healthy children. The best way to protect your child is through chicken pox immunisation.
In Singapore, parents can easily find the chicken pox jab at various clinics and hospitals. It’s important to check with your local healthcare provider or paediatrician for information on where to get the chickenpox vaccine in Singapore.
Our SBCC Baby & Child Clinics provide childhood vaccines recommended by the Ministry of Health Singapore. As our SBCC Baby & Child clinics are Baby Bonus approved, your child’s Baby Bonus can be used for their Childhood Immunisations. Call your nearest SBCC Baby & Child clinic to book an appointment for your child’s vaccination today!
SBCC Childhood Immunisation packages cover all your child’s vaccination needs based on Singapore’s National Childhood Immunisation Programme, including the chickenpox vaccine for toddlers and children.
Tele-consultation (within Singapore)
|
10 minute Consultation |
General Paediatrics Case |
Sub Specialty Case |
|
1st Consult |
$90 |
$120 |
|
Follow up |
$50 |
$80 |
Additional charges may apply for extended consultation with the doctor.
Delivery of Medication (within Singapore):
Orchard Road – $2, Tuas – $4, Sentosa and Airport – $10
*Tele-consultation (outside of Singapore) is only applicable for Sub Specialty Follow up.
In the current COVID-19 situation, parents may be hesitant to bring their little one to clinics. With this tele-consultation service, you may consult a paediatrician on non-urgent clinical matters without leaving your home.
FOLLOW-UP for stable chronic conditions such as asthma, allergic rhinitis, food allergy, eczema, constipation, juvenile arthritis, chronic urticaria
If your child is experiencing a medical emergency, please call an ambulance at 995 or make your way to the nearest Accident & Emergency department immediately. If it is not an emergency, but you/your child do not meet the requirement for telemedicine please call our clinics for an appointment. If you need mental health support, please call SOS Hotline (1800-221 4444).
1. Fill in the online registration form and make an appointment with your preferred paediatrician.
2. Complete the payment details before submitting the online registration form.
3. You will receive an SMS and Email to confirm your registration.
4. As the tele-consult request needs to be approved by the paediatrician, you will receive an SMS and Email confirming your request.
5. You will receive a video consultation link by SMS and Email when your appointment is near.
6. Click the link to start your consultation.
7. Once complete, you will receive a link by SMS and Email on the amount payable to the clinic.
8. If you have selected delivery of medication, a delivery fee will apply to your final bill amount.
A standard delivery fee of $15.00 will be charged for medication delivery within Singapore. You will receive your medication within 3 hours.
Please note the following surcharges apply to the following area:
Your medication will be delivered to your address via a courier.
At the time of registration, we charge an amount of $1 to authenticate your credit card. However, please note that this amount is immediately reversed once your request is submitted successfully.
Payment is made via your submitted credit card details at the time of registration.
| Doctor Name | Doctor Specialty (Special Interest) |
| Dr Alison Joanne Lee | Paediatric Medicine (Allergy & Immunology) |
| Dr Chan Kit Yee | Paediatric Medicine (Cardiology) |
| Dr Charmaine Teo | Paediatric Medicine |
| Dr Jenny Tang | Paediatric Medicine (Asthma, Lung, Sleep & Allergy) |
| Dr Martha Liu | Paediatric Medicine |
| Dr Nancy Tan | Paediatric Medicine (Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition) |
| Dr Natalie Epton | Paediatric Medicine (Neonatology) |
| Dr Ratna Sridjaja | Paediatric Medicine |
| Dr Wong Chin Khoon | Paediatric Medicine |
| Dr Ng Ying Woo | Obstetrics & Gynaecology* |
Thank you for choosing SBCC's Tele-Consultation service. At SBCC, we strive to provide you with a seamless and effective healthcare experience. Our Tele-consultation service is different than other providers as we can schedule a tele-consult with your preferred paediatrician through our Platform.
Please go through the below terms and conditions for our Tele-Consultation process including your rights and responsibilities of this platform. These Terms and conditions, together with our privacy policy constitute an agreement between you and Healthway Medical group.